※재료역학(mechanics of materials)이란 무엇인가?
외부 힘이 주어진 solid body의 내부 strain과 stress의 영향을 공부하는 것이다.
※Analysis & Design Mechanical Structure
Forces, Moments ↔ Stress ↔ Strain ↔Displacement, Angle
※Stress(응력) : related to force or moment → 내력에 지탱하는 성질
※Strain(변형률) : related to deformation/original stregth
※Stiffness(강성) : related to deformation → 변형에 저항하는 성질
※External Load(외부하중)의 종류
①Surface force → physical contact
- concentrated force (집중하중)
- distributed force (분포하중)
②Body force (체적)
-gravitational force (중력)
-electromegnetic force (전자기력)
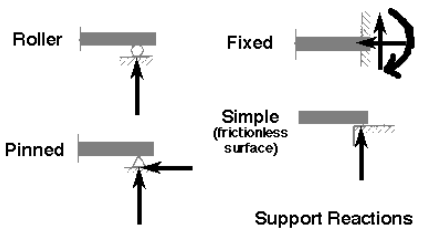
※Support Reactions (지지반력)
- 지지하는 곳으로 부터의 surface forces 또는 body간 접촉하는 포인트에서의 surface forces
- 만약 특정방향의 직선운동을 방해하는 support면 반드시 그 방향으로 힘이 생긴다.
※Equilibrium equations (평형상태 방정식)
- 평형상태 : 움직이지않고 회전하지않음 (translation없고, rotation 없음)
- Equilibrium은 force balance(translation 방지) / moment balance(rotation 방지)가 필요하다
For 2D Equilibrium
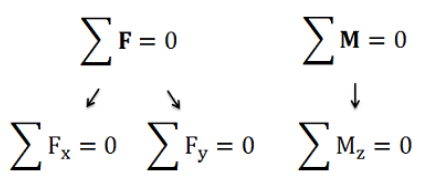
For 3D Equilibrium

※Internal Resultant Loadings (내력합)
- In 3D
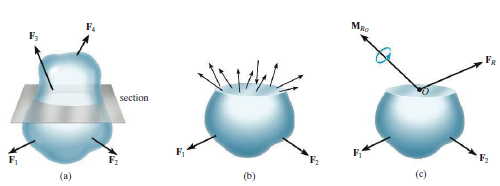
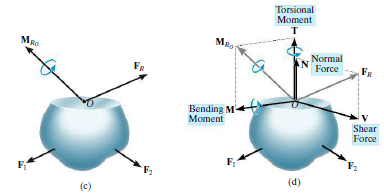
- 단면을 자르면 하나의 힘과 하나의 모멘트로 바꿔줄 수 있다. 이 때 힘은 Normal Force와 Shear Force로 나눌 수 있으며 모멘트는 Torsional Moment와 Bending Moment로 나눌 수 있다.
'전공 > 재료역학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Average Normal stress in an Axially loaded bar (1) | 2019.04.30 |
|---|---|
| Stress(응력) (0) | 2019.04.30 |

